What Is Base Rate Fallacy

Base rate fallacy or base rate neglect is a cognitive error whereby too little weight is placed on the base or original rate of possibility e g the probability of a given b.
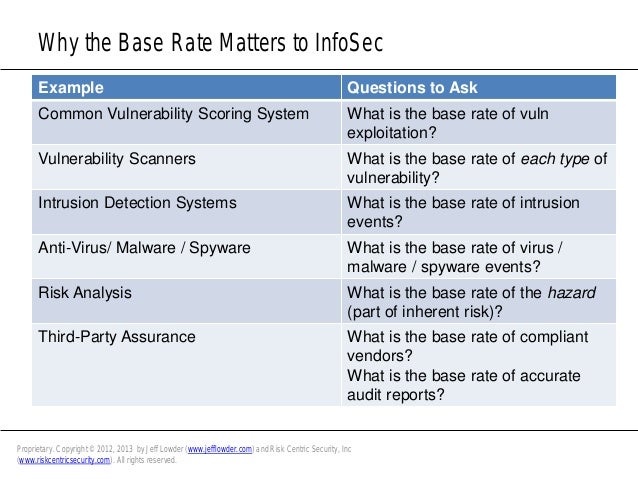
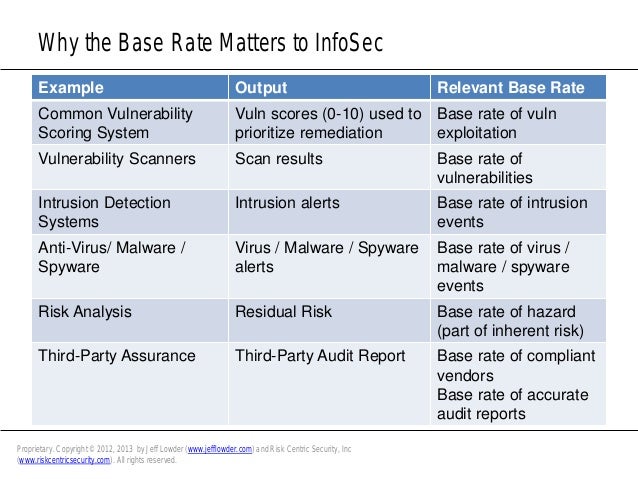
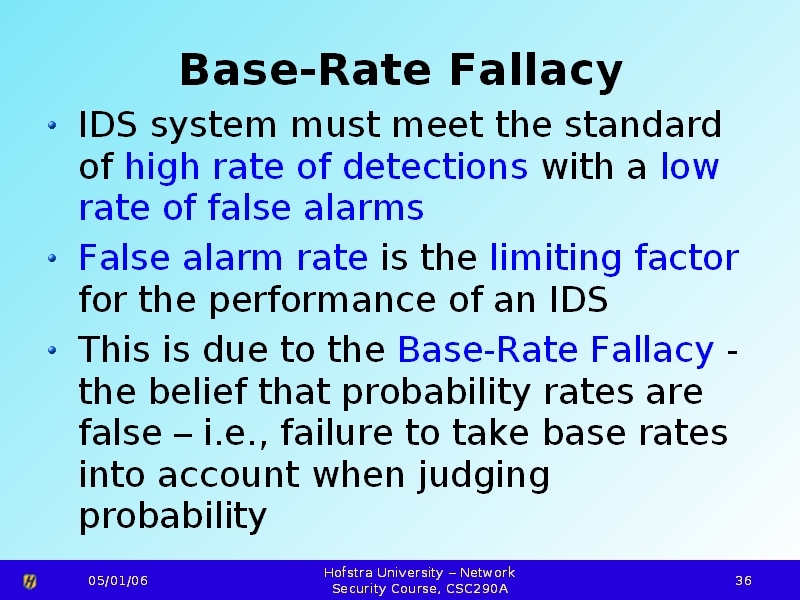
What is base rate fallacy. The key issue for social psychologists then is to understand when the base rate fallacy is likely to emerge and when it is not. The base rate fallacy also called base rate neglect or base rate bias is an error that occurs when the conditional probability of some hypothesis h given some evidence e is assessed without taking into account the base rate or prior probability of h and the total probability of evidence e. The base rate fallacy also called base rate neglect or base rate bias is a fallacy. Base rate fallacy is our tendency to give more weight to the event specific information than we should and sometimes even ignore base rates entirely.
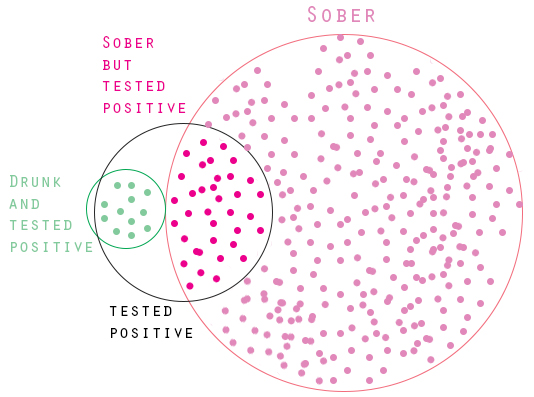
If you overlook the base rate information that 90 and then 10 of a population consist of lawyers and engineers respectively you would form the base rate fallacy. The base rate fallacy is an error in reasoning which occurs when someone reaches a conclusion that fails to account for an earlier premise usually a base rate a probability or some other statistic. Base rate fallacy is commonly studied in behavioral finance it describes the tendency of individuals to ignore statistics cognitive or rational belief and event specific information when dealing with issues. The generic information would relate to the prevalence of the condition in the population as a whole and the specific information would be that garnered from tests and examinations of one specific patient.
A simple example of this would involve the diagnosis of a condition in a patient. Base rate fallacy is a cognitive fallacy. Evidence for base rate fallacy empirical evidence suggests that base rates are sometimes completely ignored and at other times are utilized appropriately. It seeks to explain why people favor irrelevant information over rational ones and make decisions emanating from irrational beliefs.
As such the factor of base rate is not given enough weight and false conclusions may be drawn from information simply based on a particular trait and its rate of occurrence in a specific population. The base rate fallacy is committed when a person focuses on specific information and ignores generic information relating to the overall likelihood of a given event.