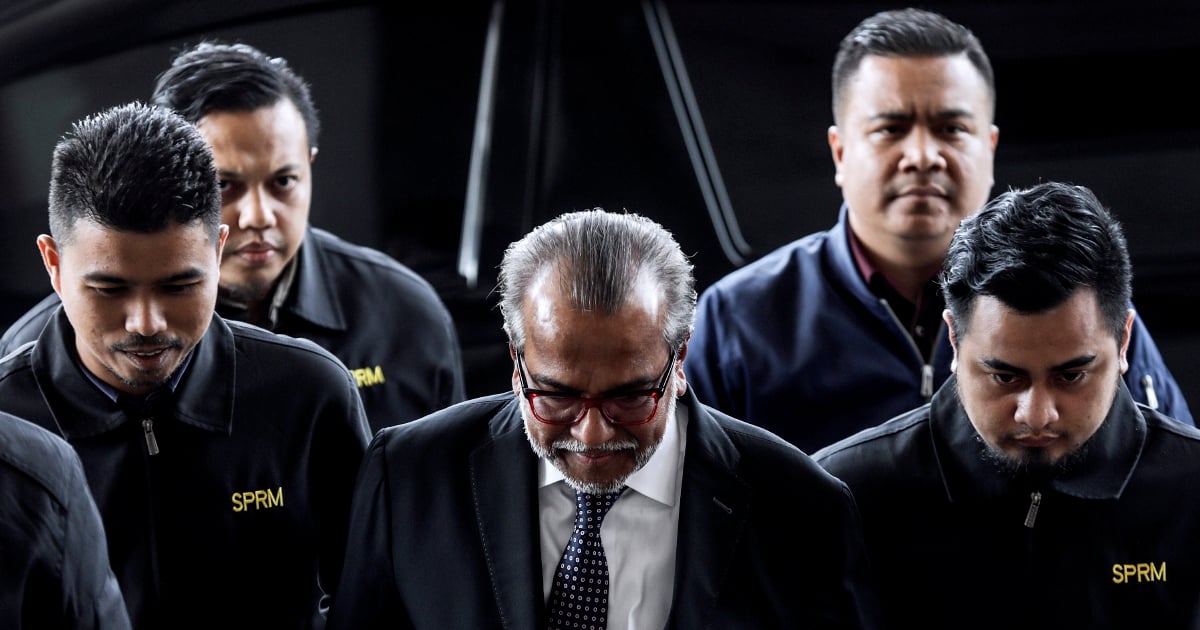
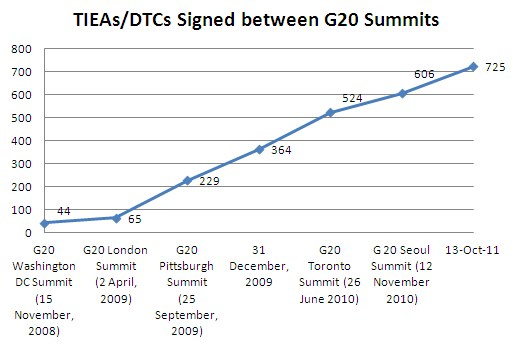
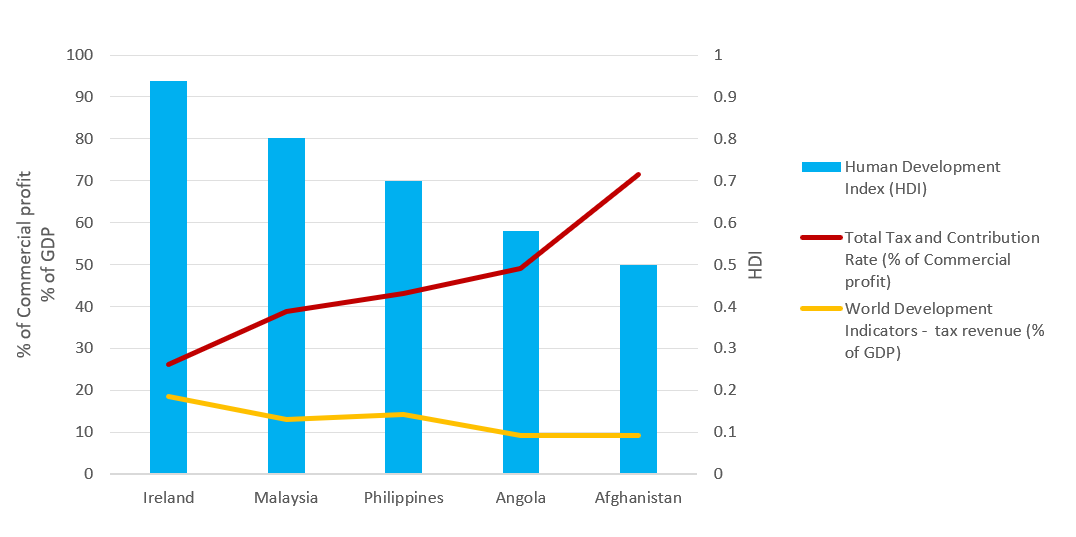
Tax Evasion Cases In Malaysia
/tax-avoidance-vs-evasion-397671-v3-5b71dfc846e0fb0025e54177.png)
2003 that investigated the influence of education on tax avoidance and tax evasion by using questioner method.
Tax evasion cases in malaysia. Investigated the phenomena of tax evasion for malaysia. Evasion is a disease and needs to be minimized so that the black economy or hidden economy can be mitigated. With this backdrop this article will examine the judicial mood in recent tax avoidance cases in malaysia namely sabah berjaya port dickson power ibraco peremba and ensco gerudi. Tax evasion anti avoidance in malaysia income tax act contains general and specific anti avoidance provision which empowers the director general to disregard schemes that are not commercially justified or are merely set up to avoid tax despite their legal form.
Section 7201 creates two offenses. As the name implies tax investigation is a method of enforcement conducted by the inland revenue board malaysia irbm to ensure accuracy of tax filing. Tax evasion through fraudulent financial reporting amongst smes in malaysia zainal abidin ngah department of graduate accounting universiti teknologi mara shah alam malaysia norashikin ismail school of accountancy universiti teknologi mara shah alam malaysia. A the willful attempt to evade or defeat the assessment of a tax and b the willful attempt to evade or defeat the payment of a tax.
Tax evasion particularly in developing countries is a debatable issue. The aim of tax investigations is to investigate taxpayers who are suspected to be involved in fraud wilful defraud or negligence in reporting their income. 2000 estimated the size of hidden income and tax evasion for malaysia. In another study kasipillai et al.
Among these studies we can point to the study of kasipillai et al. Some examples of tax fraud which may take place in malaysia are false reporting of income using a false identity for tax purposes failure to file an income tax return refusing to pay taxes or claiming personal expenses as business expenses for the purposes of reducing one s tax obligations. The maximum permissible fine is 250 000 for individuals and 500 000 for corporations.